In today’s digital landscape, cookies play a significant role in shaping our online experiences. These small pieces of data are stored on our devices by websites we visit, helping them remember our preferences, login details, and other information. However, as technology evolves and concerns over online privacy grow, the era of third-party cookies is drawing to a close. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of cookies, explain what third-party cookies are, and discuss Google’s decision to phase out these cookies.
Understanding Cookies: The Foundations of Web Browsing
Cookies, in the context of web browsing, are small text files that websites place on users’ devices. They serve as digital markers that store information related to a user’s interactions with a particular website. When you visit a website, it sends cookies to your browser, which stores them on your device. These cookies contain data such as session information, user preferences, shopping cart contents, and more. Cookies enable websites to provide personalized experiences, remember your login status, and track your activities across different sessions.
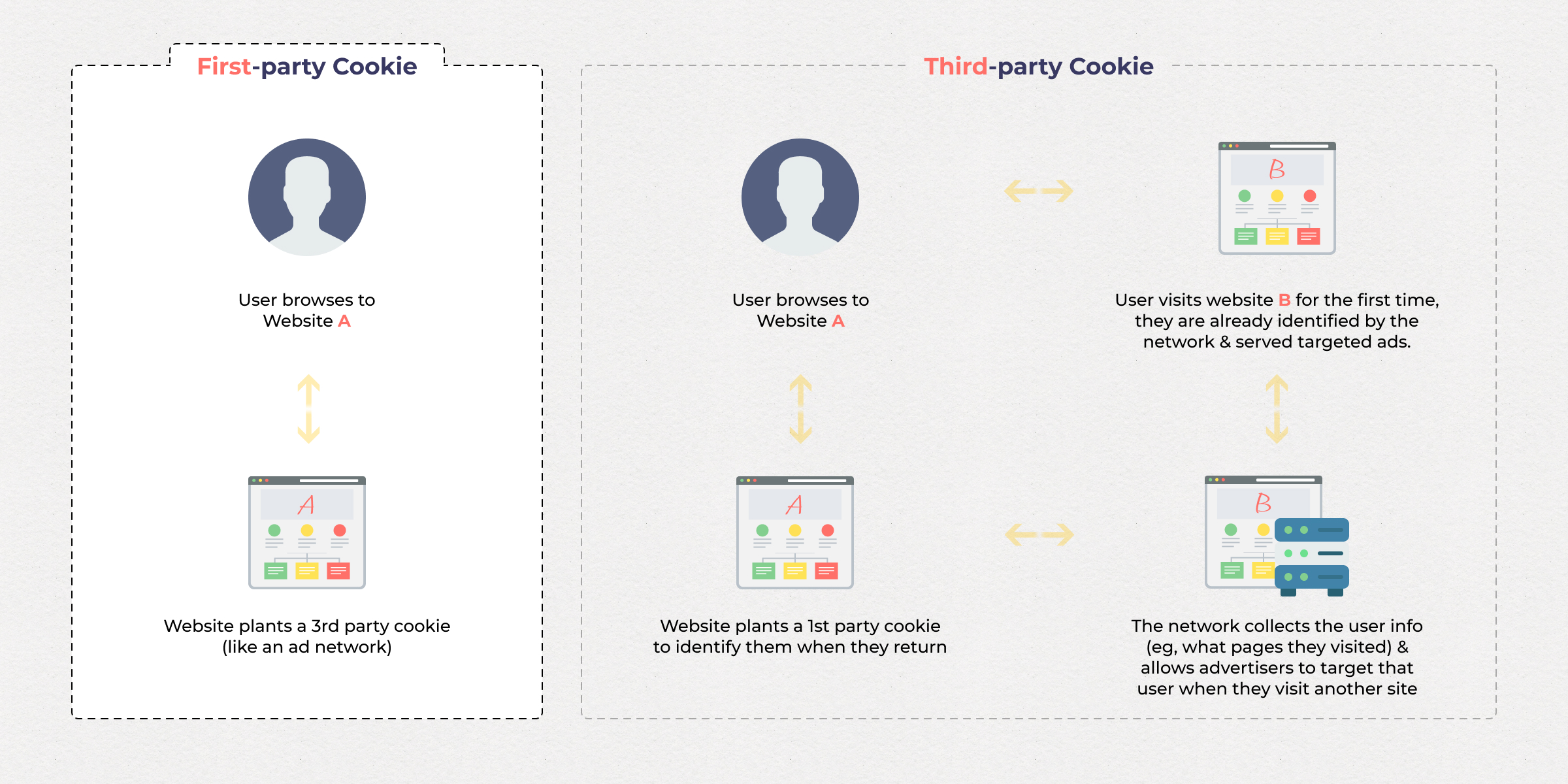
Third-Party Cookies: The Tracking Agents of the Web
Third-party cookies are a specific type of cookie that’s created by a domain other than the one you’re currently visiting. Unlike first-party cookies, which are set by the website you’re directly interacting with, third-party cookies are often created by advertisers, analytics companies, and other third-party entities that have embedded content on the website you’re visiting. These cookies are used to track your online behavior across multiple sites, allowing advertisers to serve targeted ads based on your browsing history.
The End of an Era: Google’s Ban on Third-Party Cookies
In January 2020, Google, one of the world’s largest tech companies, announced its plan to phase out support for third-party cookies in its popular web browser, Google Chrome. This decision marked a significant shift in the digital advertising landscape and sparked discussions about online privacy and user data protection. Google’s initiative, known as the “Privacy Sandbox,” aims to find privacy-friendly alternatives to third-party cookies that balance advertisers’ needs with users’ privacy concerns.
The Implications: What Happens Next?
The phase-out of third-party cookies is expected to have several implications:
- Improved User Privacy: With third-party cookies being a primary method for tracking users’ online activities, their removal will lead to enhanced user privacy. Users will have more control over their data and who has access to it.
- Changes in Digital Advertising: Advertisers heavily rely on third-party cookies for targeted advertising. Their absence will require advertisers to explore new methods for reaching their target audiences while respecting user privacy.
- Shift to First-Party Data: Companies will likely shift their focus toward collecting and utilizing first-party data, which is data directly obtained from their own website visitors. This shift can foster stronger relationships with users and provide more accurate insights.
- Innovations in Privacy-Preserving Technologies: The demise of third-party cookies is driving the development of innovative technologies that maintain user privacy while still enabling relevant ad targeting and analytics.
In conclusion, the era of third-party cookies is coming to an end, and this shift is poised to reshape the digital landscape. Google’s decision to phase out these cookies reflects the growing importance of user privacy and data protection. While the advertising industry adapts to this change, it also presents an opportunity for new and more privacy-focused approaches to online interactions.
As we move forward, it’s crucial for both users and businesses to stay informed about these changes and embrace the emerging technologies that prioritize both personalized experiences and digital privacy.



